Digital Banking: has revolutionized the financial industry, making banking services more accessible, efficient, and user-friendly. From the introduction of ATMs to the rise of mobile banking apps, the journey of digital banking is a testament to the relentless pursuit of innovation. This article explores the evolution of digital banking, highlighting key milestones and the transformative impact on consumers and financial institutions alike.
Examples of Digital Banking
1. Online Banking: Most traditional banks now offer online banking services, allowing customers to check balances, transfer funds, and pay bills from their computers. These platforms provide secure access to account information and enable users to perform various transactions without visiting a physical branch.
2. Mobile Banking Apps: Mobile banking apps have become indispensable for modern consumers. Apps from banks like Chase, Bank of America, and Wells Fargo offer features such as mobile check deposits, real-time transaction alerts, and budget tracking tools. These apps ensure that banking is just a tap away.
3. Neobanks: Neobanks, such as Chime and Revolut, operate entirely online without physical branches. They offer user-friendly apps with features like fee-free accounts, early direct deposits, and seamless international transfers. Their focus on digital-first experiences appeals to tech-savvy customers.
The Dawn of Digital Banking: ATMs
The Automated Teller Machine (ATM) marked the beginning of digital banking. Introduced in the late 1960s, ATMs provided customers with the convenience of withdrawing cash, checking account balances, and performing other basic banking transactions without visiting a bank branch. The first ATM was installed by Barclays Bank in London in 1967, revolutionizing the way people accessed their money.
ATMs quickly gained popularity due to their 24/7 availability, reducing the need for customers to rely solely on bank branch hours. Over time, ATMs evolved to offer a wider range of services, including cash deposits, bill payments, and even loan applications. This shift not only enhanced customer convenience but also allowed banks to streamline operations and reduce costs.
Online Banking: The Next Frontier
The advent of the Internet in the 1990s paved the way for online banking. Banks began offering online services that allowed customers to perform a variety of transactions from the comfort of their homes. Online banking provided access to account information, fund transfers, bill payments, and loan applications, all through a secure web portal.
The introduction of online banking brought several advantages:
- Convenience: Customers can access their accounts anytime, anywhere.
- Cost-Efficiency: Banks could reduce operational costs by moving transactions online.
- Enhanced Services: Banks could offer a broader range of services without physical constraints.
Despite initial concerns about security, advancements in encryption and authentication technologies helped build customer trust in online banking. By the early 2000s, online banking had become a standard offering for most financial institutions.
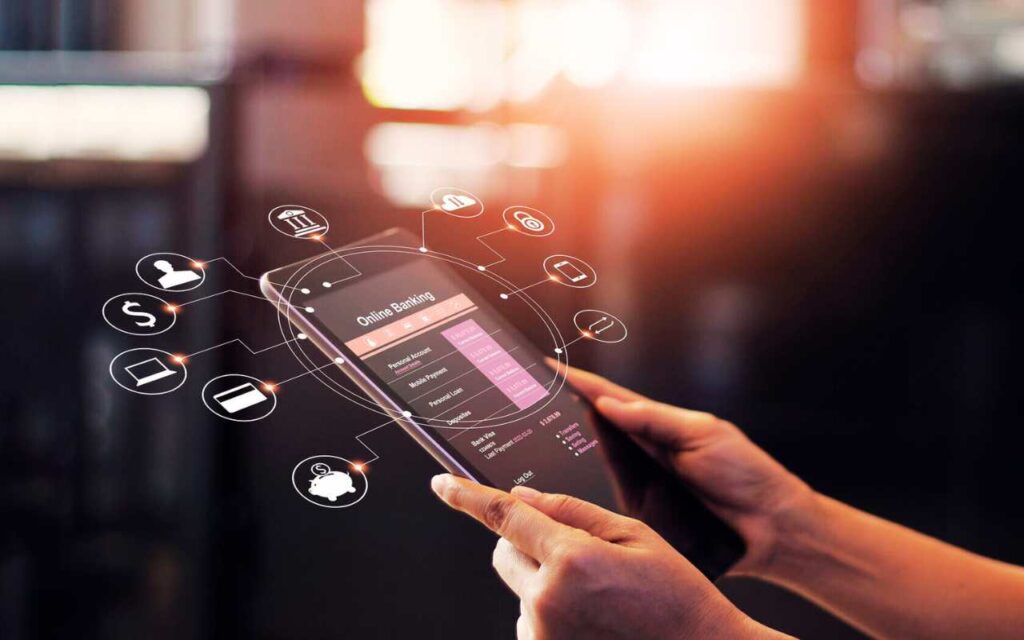

Mobile Banking: Banking on the Go
The proliferation of smartphones in the late 2000s and early 2010s gave rise to mobile banking. With mobile apps, customers could carry their banks in their pockets, accessing banking services on the go. Mobile banking apps offer a wide range of functionalities, including:
- Real-Time Notifications: Instant alerts for transactions and account activities.
- Mobile Deposits: Depositing checks by taking a photo with a smartphone camera.
- Fund Transfers: Sending money to other accounts or individuals quickly and easily.
- Budgeting Tools: Integrated features to help customers manage their finances.
Mobile banking apps significantly enhance user experience by providing intuitive interfaces and seamless access to banking services. The use of biometrics, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, further improved security, making mobile banking both convenient and safe.
The Rise of Fintech: Disrupting Traditional Banking
The emergence of fintech (financial technology) companies has further accelerated the evolution of digital banking. Fintech startups leverage technology to offer innovative financial services, often challenging traditional banks. These companies focus on specific areas such as payments, lending, investing, and personal finance management.
Key innovations introduced by fintech include:
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Payments: Apps like PayPal, Venmo, and Zelle allow users to send money directly to each other.
- Robo-Advisors: Automated investment platforms that provide personalized financial advice and portfolio management.
- Digital Wallets: Services like Apple Pay, Google Wallet, and Samsung Pay enable secure, contactless payments. (Digital banking app)
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: Decentralized technologies that offer new ways to transact and store value.
Traditional banks have responded by partnering with fintech companies, acquiring them, or developing their own digital solutions to stay competitive. This collaboration has led to a more dynamic and innovative financial ecosystem.
Tim Walz: A Dedicated Public Servant and Governor of Minnesota
What is Digital Banking UNFCU
Digital banking at the United Nations Federal Credit Union (UNFCU) revolutionizes the way members manage their finances. It provides a seamless, secure platform to perform a range of banking activities online or via mobile apps. Members can check account balances, transfer funds, pay bills, and deposit checks remotely.
UNFCU’s digital banking emphasizes user-friendly interfaces, advanced security features, and 24/7 accessibility, ensuring members can handle their banking needs anytime, anywhere.
Whether you’re at home or traveling globally, UNFCU’s digital banking offers convenience and efficiency, making it a valuable tool for modern financial management.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming digital banking by enabling more personalized and efficient services. Banks use AI and ML for:
- Customer Service: Chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 support, answering queries and performing transactions.
- Fraud Detection: Advanced algorithms analyze transaction patterns to detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Personalized Financial Advice: AI-driven tools offer tailored recommendations based on customers’ financial behavior and goals.
- Risk Management: Predictive analytics help banks assess credit risk and make informed lending decisions.
AI and ML are enhancing the customer experience by making banking more intuitive and responsive to individual needs. These technologies also help banks optimize their operations and reduce costs.
The Future of Digital Banking
The future of digital banking promises even more innovation and integration. Some trends to watch include:
- Open Banking: Allowing third-party developers to build applications and services around financial institutions, promoting greater competition and innovation.
- Blockchain and Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Expanding the use of blockchain for secure, transparent, and efficient transactions.
- Voice Banking: Utilizing voice assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant for banking transactions.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity: Continual advancements in security technologies to protect against emerging threats.
As technology continues to evolve, digital banking will become even more integral to our daily lives. Financial institutions must stay agile, adopting new technologies and adapting to changing customer expectations to thrive in this dynamic landscape.
Conclusion
The evolution of digital banking from ATMs to mobile apps highlights the transformative power of technology in the financial industry. Each advancement has brought greater convenience, efficiency, and security to banking services, reshaping the way we manage our finances. As we look to the future, the ongoing integration of AI, blockchain, and other cutting-edge technologies will continue to drive innovation, ensuring that digital banking remains at the forefront of the financial revolution.




2 Comments